Scenario:
A couple of stooge network engineers are trying to configure EIGRP over the frame-relay network. They read all about frame-relay, EIGRP and split-horizon and decided it sounded like a good idea to use sub-interface. Unfortunately things are not working as they should. Do you think you can help them out?
Goal:
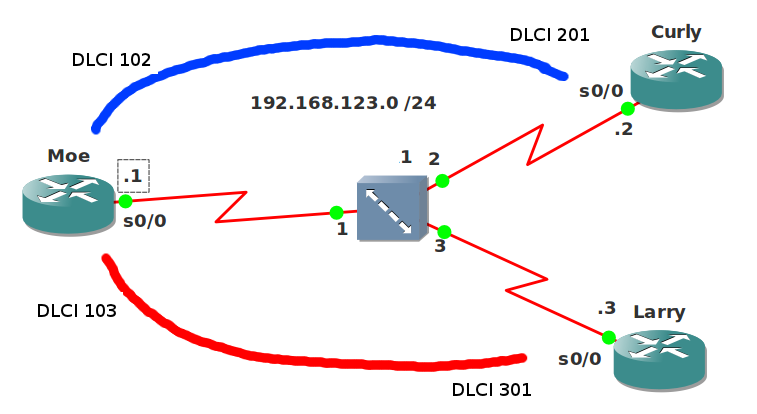
- All IP addresses have been preconfigured for you as specified in the topology picture except for router Moe.
- Every router has a loopback0 interface:
Moe: 1.1.1.1 /24
Curly: 2.2.2.2 /24
Larry: 3.3.3.3 /24 - You are not allowed to make any changes to the frame-relay configurations.
- Configure a multipoint sub-interface on router Moe.
- Configure EIGRP AS 123 on all routers and advertise the loopback interfaces.
- Ensure router Curly and Larry can see each other’s loopback interfaces. Test this by sending a ping that is sourced from the loopback0 interfaces and destined for the other loopback0 interface.
It took me 1000s of hours reading books and doing labs, making mistakes over and over again until I mastered all the routing protocols for CCNP.
Would you like to be a master of routing too? In a short time without having to read 900 page books or google the answers to your questions and browsing through forums?
I collected all my knowledge and created a single ebook for you that has everything you need to know to become a master of routing.
You will learn all the secrets about EIGRP, frame-relay setups and more.
Does this sound interesting to you? Take a look here and let me show you how to Master CCNP ROUTE
IOS:
c3640-jk9s-mz.124-16.bin
Topology:
Configuration Files
You need to register to download the GNS3 topology file. (Registration is free!)Once you are logged in you will find the configuration files right here.

The How to Master series helps you to understand complex topics like spanning-tree, VLANs, trunks, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP and more.
Written by René Molenaar - CCIE #41726


Umm last step.. where is router “joe and jack”?
Hi Terrelle,
Just fixed the article…too much copy/paste action ;D
Rene
Hey Rene will you be posting up youtube video solutions for these labs — I noticed some of the EIGRP do not have them posted.
Thanks,
WZ
Hi William,
I will once i’m finished with some more labs…I’m on a labbing spree and once i’m done I’ll start recording the videos.
Let me give you one hint for this one…check what the difference is between a physical multipoint interface and a sub-interface multipoint and how it affects EIGRP.
Rene
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtPNnS6x6NI&feature=related
Hi Rene
First of all, I’d like to thank to you for every thing that you are doing here.
What can we do in this scenario to ping loopbacks without need for specifying the source of ping packets?
Good Luck.
Akbar
Hi Akbar,
If you don’t specify the source IP address for the ping then it will be sourced from the IP address on the interface. If this doesn’t work you’ll have to create some additional frame-relay map statements so the routers know how to reach each others IP addresses.
Rene
Yes, by adding a FR map statement on spoke routers, it works…
Thank you Rene 🙂
Akbar
Good Job Akbar! Make sure that whenever you have reachability issues that you check if the next hop IP address in the routing table is reachable or not.
Keep up the good work. It great to do read the book ( master ccnp route) and do the labs.
Thanks
Rakesh
Thanks Rakesh for your comment!
Rene,
This site is the best and gns3 is a great product. I purchased your ccnp router and switch ebook and I find it full of wealth of information and clarity on once difficult concepts. I just passed my icnd2 exam and working towards my ccnp next.
Thank you
Thanks for your comment, it’s much appreciated to hear that my material is useful!
Hi Rene,
I finished this lab and after changing subinterface on the Moe router to the physical one, that’s what I found out. Split horizon is enabled on physical and subinterfaces by deafault. Split horizon is disable on physical interfaces by default only for RIP, not for EIGRP. If you have a router with IOS version 15.x, you can check it out by issuing the “show ip eigrp interface detail sx/x command and you’ll be able to see an output like this:
R2#sh ip eigrp interfaces detail s1/0
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se1/0 1 0/0 77 0/15 335 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
[b]Split-horizon is enabled[/b]
Next xmit serial
Whereas, the output of the “show ip int sx/x” command shows:
Security level is default
[b]Split horizon is disabled[/b]
ICMP redirects are always sent
So, without disabling split horizon on the physical interface of the HUB router I couldn’t get all routes on my spoke routers and ping didn’t work.
I’m reading the Implementing Cisco IP Routing Foundation Learning Guide book and now I really know that statement about that split horizon is disabled by default on physical frame-relay interfaces and no other measures has to be done other than enable EIGRP on the specific interface is in fact, totally wrong.
In the end of my investigation I figured out that there is not difference between configuration EIGRP on physical multipoint interface or subinterface multipoint.
Rene, thanks a lot!
Hi Slz,
Thanks for your post and sharing this. It will be useful for other people as well. It’s always good to remember to check split horizon for RIP or EIGRP on the interface, it’s one of those things that are easy to forget. I’m not sure but it’s possible that split horizon is enabled/disabled by default on certain IOS versions.
Rene
I’ve tried different routers with various IOS versions, but behavior of EIGRP has been the same, as I’ve described above. Perhaps, EIGRP worked, as covered in the book in much earlier IOS versions, as you’ve noted, but I don’t know and haven’t that experience. And one more thing, the real state of split horizon I could only see from the output of the router which run IOS version 15.x. The output of the “ip eigrp interface detail sx/x” command issued on some routers with earlier IOS versions didn’t have the string described the current state of split horizon.
I’ve just read Cisco guide about configuring EIGRP and found that split horizon is enabled on all interfaces by default starting from IOS version 12.2 – [url=http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/ip/configuration/guide/1cfeigrp.html]Disabling Split Horizon[/url]
Thanks for sharing this!
Hi Rene,
Any idea when the video solution for this lab will be available ?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtPNnS6x6NI&feature=related
it is good?
Nailed it!
Thanks Renee, these labs and your Mastering Route book are faaar better than the video series my company paid waaay to much for.
All IP addresses have been preconfigured for you as specified in the topology picture except for router Moe.
I have no luck getting the pre-configured part.
Thanks
Anam
Hi all,
I am succeeded to get the ping as mentioned . But failed to get self ping. ie , from Moe no ping response from 192.168.123.1 and same situations for other 2 routers. what might be the cause,
Moe,
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
no ip split-horizon eigrp 100
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay interface-dlci 102
frame-relay interface-dlci 103
Curly
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
no ip split-horizon eigrp 100
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 201
frame-relay interface-dlci 201
Larry
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
no ip split-horizon eigrp 100
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 301
frame-relay interface-dlci 301
Thanks ..
Hey nraam
I think you are missing an extra frame relay map statement on both Curley and Larry
Curley
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 201 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 201 broadcast
Larry
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 301 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 301 broadcast
Hi Rene,
Nice stuff!
Is it possible to get the configuration of the labs in pdf format?
Thanks!
Hi Rene!
Thanks for your efforts, I’d like to thankyou and to ask one question regarding this lab.
I struggled alot but managed to hit the targets. My question is that why I’m unable to ping from router LARRY to CURLY’s ip.
i.e 192.168.123.3 to .123.2 and vice versa too.
Althogh on both Curly and Larry shows that they know about 192.168.123.0/24 network.
Thanks in advance.. and keep up the good work
God Bless you
Hi Rene!
Thanks for your efforts, I’d like to thankyou and to ask one question regarding this lab.
I struggled alot but managed to hit the targets. My question is that why I’m unable to ping from router LARRY to CURLY’s ip.
i.e 192.168.123.3 to .123.2 and vice versa too.
Althogh on both Curly and Larry shows that they know about 192.168.123.0/24 network.
Thanks in advance.. and keep up the good work
God Bless you
Create 2 multi-point interfaces with 192.168.123.1 ip address and issue separate frame-relay mappings . This will resolve the issue immediately if there is no reach-ability
Awesome Rene,
Eventhough I’m CCNA Certified, all your labs are interested and Challenging. I have your CCNP Books, and Finished Switching 2 weeks back, Now started Routing.
Thanks for all the Work Done..
Any Plans on Releasing the Book for CCIE
Hi Winston,
Glad to hear that you like them 🙂 Good luck with the ROUTE exam, there’s a lot of stuff to learn.
Right now I am working on my “How to Master CCIE Written” book, hopefully it’s done in a couple of weeks. Some of the blog posts on networklessons.com will be used in the book.
Rene
Hello René, ow are you doing today ?
Look, could you clarify me why I am not able to ping the loopbacks when I don’t use the loopback as the source interface ? Look at this example below :
Curly#ping 3.3.3.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 3.3.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
…..
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Curly#ping 3.3.3.3 source loopback 0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 3.3.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 2.2.2.2
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 60/93/152 ms
Curly#
Here’s why you need the “source” in the ping command, please correct me if I’m mistaken:
Without a source interface, the ping command will use the outgoing interface’s IP. This source IP will be the IP for return traffic. On a frame relay multipoint network, the layer 2 to layer 3 is performed by the frame-relay map command, not by arp.
In our scenario, the return address does not have a layer 2 to layer 3 mapping, so it cannot find the return path. Sourcing the ping from the loopback routes traffic via the hub (192.168.123.1) for which there IS a layer2 to layer 3 mapping, so the ping succeeds.
Here is my Solution that worked well:
hostname Moe
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/0.1 multipoint
ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
no ip split-horizon eigrp 123
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 102 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 103 broadcast
!
!
router eigrp 123
passive-interface Loopback0
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
hostname Curly
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/1
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/1.1 point-to-point
ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
frame-relay interface-dlci 201
!
!
router eigrp 123
passive-interface Loopback0
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
!
hostname Larry
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex half
!
!
interface Serial1/2
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/2.1 point-to-point
ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
frame-relay interface-dlci 301
!
interface Serial1/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
!
router eigrp 123
passive-interface Loopback0
network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
!
Here is my config , it worked well but I have an issue, I cant ping any router’s physical interface IP from it’s self, i.e pinging MOE: 192.168.123.1 from Moe’s console. don’t know why though any advice would help or is this the normal working behavior?
MOE
hostname Moe
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
!
!
ip cef
!
!
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
no frame-relay inverse-arp
!
interface Serial0/0.1 multipoint
ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
no ip split-horizon eigrp 123
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 102 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 103 broadcast
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/2
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
router eigrp 123
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
!
CURLY
hostname Curly
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
!
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 201 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 201 broadcast
frame-relay interface-dlci 201
no frame-relay inverse-arp
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/2
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
router eigrp 123
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
LARRY
hostname Larry
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
!
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 301 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 301 broadcast
frame-relay interface-dlci 301
no frame-relay inverse-arp
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/2
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
router eigrp 123
network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.123.0
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
I’m struggling with this one. I’ve tried the broadcast keyword in my frame map statements, clearing learned iARP entries, and even statically defining neighbors. I can ping from router to router, but I can’t form any EIGRP neighborships if I use physical interfaces on Moe. Is this an issue with GNS? I did find I had to clear all slots in my 3640 router in GNS3 settings before I could even get dynamips to properly start and allow me console view.
I had used Frame Relay routes on the FR switch and frame-relay map ip command to achieve the working. Also had to disable split horizon on the multipoint interface. Some partials configs shown below.
Frame Relay Switch:
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 102 interface Serial0/1 201
frame-relay route 103 interface Serial0/2 301
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 201 interface Serial0/0 102
frame-relay route 301 interface Serial0/0 102
!
interface Serial0/2
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 301 interface Serial0/0 103
frame-relay route 302 interface Serial0/0 103
!
===============
MOE:
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial0/0.123 multipoint
ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
no ip split-horizon eigrp 1
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.2 102 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.3 103 broadcast
!
CURLY:
interface Serial0/1
ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
LARRY:
interface Serial0/2
ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
serial restart-delay 0
!