Scenario
As a fan of comedy movies you are making sure your network is optimized so you can send videos without any disruptions in the network. You heard EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a good choice since the failover speed is low and it’s able to load balance between unequal paths. There are 3 different serial links and you want to make the optimal use of them. Whenever a link fails you need to make sure the routing protocol converges as soon as it can….surely you can solve this!
Goal:
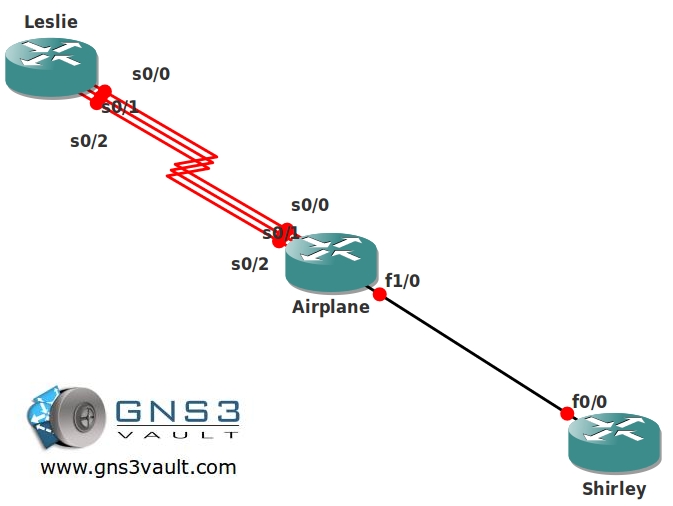
- All IP addresses have been preconfigured for you:
Leslie: 192.168.X.1 /24 (.1 – .2 & .3 on serial links)
Leslie: L0: 1.1.1.1 /24Airplane: 192.168.X.2 /24 (.1 – .2 & .3 on serial links)
Airplane: F0/0:192.168.23.2 /24Shirley: F0/0: 192.168.23.3 /24
Shirley: L0: 3.3.3.3 /24 - Configure EIGRP AS123 on all routers, advertise all networks.
- You are not allowed to make changes to the K values or Bandwidth on interfaces.
- Disable EIGRP auto-summarization.
- Make sure that only S0/0 and S0/1 are visible in the routing table and used for sending traffic.
- When S0/0 and S0/1 both fail make sure that S0/2 takes over.
It took me 1000s of hours reading books and doing labs, making mistakes over and over again until I mastered all the protocols for CCNA.
Would you like to be a master of networking too? In a short time without having to read 900 page books or google the answers to your questions and browsing through forums?
I collected all my knowledge and created a single ebook for you that has everything you need to know to become a master of CCNA.
You will learn all the secrets about EIGRP, successors, feasible successors, path selection and more.
Does this sound interesting to you? Take a look here and let me show you how to Master CCNA!
IOS:
c3640-jk9s-mz.124-16.bin
Topology:
Video Solution:
Configuration Files
You need to register to download the GNS3 topology file. (Registration is free!)Once you are logged in you will find the configuration files right here.

The How to Master series helps you to understand complex topics like spanning-tree, VLANs, trunks, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP and more.
Written by René Molenaar - CCIE #41726


How can we implement the failover from S0/0 and s0/1 to s0/2? Anybody familiar with the commands?
Read up on maximum-paths and variance.
@ Deep: first you configure variance to increase the FD,
next you cut down the max no of routes allowed by limiting with max-path option.
Wow rene, i thought I’d covered these two topics pretty well for my exam, considering the no of experiments I’d done.
but it never struck me to test both these features at the same time.
thanx!
Glad you liked it, it’s fun to mix a few things together 8)
Easy peasy lemon-squeezy. Check show ip eigrp 123 topology all-links to estimate variance required x7 as largest cost is 21154560 and current FD is 3142400. and change maximum-paths to 3 also.
Hi Rene,
In goals you have mentioned that if s0/0 or s0/1 got fails s0/2 needs to takeover.But in video solution you have failed both.
I tried to implement this but facing peculiar problem :
If S0/0 got fails S0/2 will occupy it’s position but if S0/1 fails it is not coming up. Do you have any idea bout this ??
Hi Sudheer,
You are right, this is a little confusing. I just changed the goal to “When S0/0 and S0/1 both fail make sure that S0/2 takes over”
S0/0 = successor route
S0/1 = feasible successor route
S0/2 = never shows up in routing table.
When S0/0 and S0/1 both fail there will be a new calculation and S0/2 will be installed as a successor route.
When either S0/0 or S0/1 are down S0/2 can become a feasible successor, it will never be the successor since it has the worst metric of all three interfaces.
It’s still possible to configure your routers that S0/2 will take over when either S0/0 or S0/1 fail but it’s not an EIGRP solution. You can play around with the “backup interface” command for that.
Does this make sense? If now let me know 🙂
Rene
this lab is cool. thanks Rene.
Regards/Asif
Thanks Asif!
Hi Rene,I achieved the goal by playing with metrics so that only S0/0 & S0/1 shown up in routing table and when both S0/0 & S0/1 fails S0/2 takes over.But the problem is when S0/0 & S0/1 comes up ( by giving no shut command) int S0/2 is still shown in routing table.how could this be possible??
FAISAL
Hi Faisal,
Sorry for not responding earlier, I’ve been very busy migrating the website. To answer your question I would like to see 3 things:
– The output of the routing table.
– The output of the EIGRP topology table.
– Your EIGRP configuration from the running-config.
By default this is how EIGRP behaves:
– First it will choose a successor route and it will look for feasible successors.
– The successors and feasible successors will show up in the EIGRP topology table.
– Only the successor table shows up in the routing table.
– In case you have two equal paths you will see both entries in the routing table.
– Once the successor fails EIGRP will copy/paste the best feasible successor from the EIGRP topology table into the routing table.
EIGRP can also load-balance over feasible successors, in this case both the successor AND the feasible successor will show up in the routing table. You can use the "variance" command to achieve this.
In your case you should check your EIGRP topology table and look which route is the "successor" and which one(s) are feasible successors.
This was an excellent lab. Thanks Rene.
Thank you Rak!
Cool stuff man. Tnx a mil for all these labs
You are welcome, thanks for your message!
Hi Rene,
before applying varience on leslie router my succesor for 3.3.3.3 was s0/0 192.168.1.2
but
after applying varience 2 on on leslie router my succesor for 3.3.3.3 was s0/0 & S0/1
but
whenever i ping from leslie to 3.3.3.3 it takes s0/1 prior to s0/0
why this is happening
Config on leslie
LESLIE#sh run | s eigrp
router eigrp 123
variance 2
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
network 192.168.2.0
network 192.168.3.0
no auto-summary
Routing Table:
D 3.3.3.0 [90/5642496] via 192.168.2.2, 00:12:53, Serial0/1
[90/3142400] via 192.168.1.2, 00:12:53, Serial0/0
Another great lab 🙂
I just want to check to see if I did this correctly. I see a lot of comments discussing methods that I did not take, but mine seems to work and would like input please.
All I did, was check the interfaces and noticed that the bandwidth was already set for these showing:
S0/0 = 1024
S0/1 = 512
S0/2 = 128
Delay for all 3 were equal .
I set the eigrp max paths to 2 (since S0/0 and S0/1 needed to be used together). Since 512 is half of 1024 I set the variance to 2 allowing them to load balance. The S0/2 interface BW is less than half of S0/1 so when I killed S0/0 it didn’t automatically pick up the S0/2 for the balancing. Once I killed S0/1, it picked up the S0/2. I re-enabled the S0/0 and that one became the path, and once S0/1 was re-enabled, it again load balanced between S0/0 and S0/1.
So to summarize my actions, all that was done was set max paths and variance both to 2.
Please let me know if I missed anything or if this was done wrong. Thank you!
[b]To BMinnix:[/b]
Setting the maximum-paths 2, is what I would consider best practice in the real world. This way you can avoid any un-wanted unequal cost load sharing. However if you issue [b]sh ip protocols[/b] you will notice the default maximum-paths is usually 4, so lowering the maximum-paths to 2 is not a neccesary step. (Just best practice in my opinion) Also something to keep in mind, the maximum-paths might vary depending on the IOS so be careful.
[b]Now something for everyone:[/b]
How can you accomplish this without making any confiugration changes on the [b]Leslie[/b] router with the exception of enabling EIGRP and disabling auto-summary? -This is a good CCIE question 🙂 -And you cannot directly change K values used within EIGRP, nor can you change any ‘metric’ values (Bandwidth/delay) on the interfaces on any of the three routers.
Go!
Below condition is specified in the lab but when i checked the configs i found the bandwidth on interfaces have been change that doesn’t meet the below criteria.
You are not allowed to make changes to the K values or Bandwidth on interfaces.
I chose a different approach because of this criteria. I have changed the delay on interface s0/2 of Leslie as it was not mentioned for this in the lab.
This changed the metric calculation of interface s0/2 and its not successor. Below output is when s0/0 and s0/1 are down
Leslie#sh ip route eigrp
D 3.3.3.0 [90/3091456] via 192.168.3.2, 00:00:17, Serial0/2
D 192.168.23.0/24 [90/2963456] via 192.168.3.2, 00:00:17, Serial0/2
Below is output when s0/0 and s0/1 are up
Leslie#sh ip route eigrp
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 3.3.3.0 [90/2323456] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/1
[90/2323456] via 192.168.1.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/0
D 192.168.23.0/24 [90/2195456] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/1
[90/2195456] via 192.168.1.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/0
Please share your thoughts on this.
Part on my challenge was you can not make configuration changes to Leslie, aside from enabling EIGRP for all interfaces and turning off auto-summary.
So changing the delay on leslie is a configuration change 🙂
And you can’t change any K values or metrics directly on interfaces (bandwidth/delay/load,etc) on any routers.
please can you help me with IOS he is using
Im sorry but I cant get these files to load even though I have followed your instructions in this link http://gns3vault.com/Faq/203-bad-number-of-parameters-1-with-minmax22.html. When I open your .net file in notepad stuff is just everywhere it no format to it. I even viewed your video and Im still getting the same error.
You should open it in wordpad, not notepad. There’s no structure in notepad.
I was able to get my lab going. All that I used was the variance command never used the maximum path command and everything work like a champ. Even when I shut down s0 and 1, s2 ended up kicking in. I never seen in the instructions to use the maximum path command not sure why people used it in the first place. I guess in the real world we are suppose to be using it perhaps, Rene?
By default only the successor will be in the routing table unless you have 2 successors. The maximum path command will set a limit to the number of successors it will use to load-balance.
The variance command we use to load balance over feasible successors as well.
Great lab Rene.
A couple of questions.
1/ The video solution you provided shows different bandwidths configured on the interfaces but in the lab you say we’re not allowed to make any changes to the k values & bandwidth?
2/ Can’t seem to understand how you arrived at the variance multiplier of 2.
3/ Thought the network 0.0.0.0 was only used for default routes so learnt something new
4/ From my CCNA, I remember having to configure clock rate on the DCE end to get connectivity, but this wasn’t the case with GNS3, also a ‘sh controllers serial’ shows all interfaces as DCE. Not sure if it’s something to do with gns3, just curious
Finally,I took a different approach and ‘seemed’ to arrive at the solution (maybe). Since the metric was same on all 3 serial links, all 3 routes appear in the routing table & topology table
[code]Airplane#sh ip eigrp topo
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(123)/ID(192.168.23.2)
Codes: P – Passive, A – Active, U – Update, Q – Query, R – Reply,
r – reply Status, s – sia Status
P 1.1.1.0/24, 3 successors, FD is 1889792, U
via 192.168.3.1 (1889792/128256), Serial1/1
via 192.168.1.1 (1889792/128256), Serial1/2
via 192.168.2.1 (1889792/128256), Serial1/0[/code]
To ensure that ‘S0/0 and S0/1 are visible in the routing table and used for sending traffic.’, I increased the delay on serial 1/2 on Airplane to 30000usec so both routes (successors) are visible in the routing table
[code]Airplane#sh ip ro
Codes: C – connected, S – static, I – IGRP, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2, E – EGP
i – IS-IS, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2, ia – IS-IS inter area
* – candidate default, U – per-user static route, o – ODR
P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 1.1.1.0 [90/1889792] via 192.168.3.1, 00:00:27, Serial1/1
[90/1889792] via 192.168.2.1, 00:00:27, Serial1/0[/code]
When I shutdown S0/0 and S0/1, S0/2 takes over. No variance configured mainly because I can;t quite figure out how to calculate the variance multiplier..
I look forward to your comments.
thanks
1) I don’t think Rene mentions anything about BW on his video solution.
2) if you llok for example R1
P 3.3.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3142400
via 192.168.1.2 (3142400/156160), Serial0/0
via 192.168.2.2 (5642496/156160), Serial0/1
via 192.168.3.2 (20642560/156160), Serial0/2
you want to make use s0/0 and s0/1 only. as it is s0/1 and s0/2 are feasible successors right?
to make only s0/1 a successor but not s0/2 you need to use variance so as
variance x FD > feasible’s successor’s FD or
3142400 x FD > 5642496
the smallest variance you can achieve that is 2 which ensures that s0/1 becomes successor but not s0/2
3) was also new to me so thanks Rene 🙂
4) i had the same question. i think it has to do with GNS3. i believe clock rate has a meaning only to real equipment
Rene states that we can’t change metric so look at my example above and i believe you will understand now how variance works
hi rene,
i changed the variance to 2 and nothing happened in the AIRPLANE routing table until i used the ‘clear ip eigrp neighbors’ command. is this normal? has anyone else had this issue? thanks.
-a
@Alien you are right. after spending so much time to figure out I used the clear ip eigrp ei command and it showed the variance.
it’s faily simple, use variance to allow all 3 serial’s to load balance, then use maximum paths 2 so that only two work at a time.
Hi Rene
Don’t you think the route through S 0/0 will be successor and remaining both routes [ S 0/1 & S 0/2] will be feasible successors….
The advertised distance/reported distance of the other two routes is less than the Feasible distance of the successor
And if it is the case then even if both s 0/0 and s 0/1 fails then s0/2 will take over and EIGRP will not run to calculate the route as route through S 0/2 is also feasible successor
Great LAB.. I scratched the stuff again. 🙂
Hello Rene,
Why is it that the variance command only affects the route table of the router were the command is issued ?
Is because the feasible distances are local to the routers ?
Thanks for the lab, and nice new website layout 😉
Pedro
Each router computers FD differently, so yes.
Rene
can i know which telnet client you are using?
I like all of your movie references you’re naming the routers after in a lot of the labs. haha!
Correct me if I am wrong
As what we can achieve the goal by changing BW to
S0/0=1024
S1/1=512
S1/2=460
If any one have idea about Backup interface and Primary interface do share your knowledge