Scenario:
As the senior network engineer for a Dutch fishing company you are responsible for connecting all the different branch offices to the main network. The WAN technology you are using is Frame Relay, and you need to run OSPF over this WAN connection.
Goal:
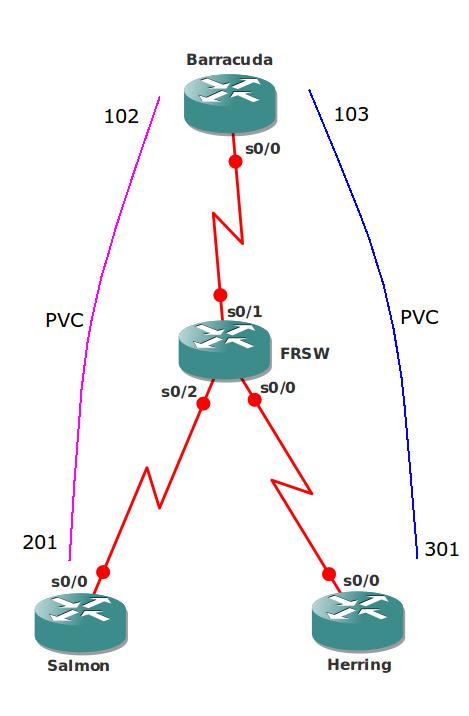
- The frame-relay switch has been preconfigured for you, as you can see in the topology picture the following PVC’s has been configured:
Router Barracuda to Salmon:
Barracuda: DLCI 102
Salmon: DLCI 201Router Barracuda to Herring:
Barracuda: DLCI 103
Salmon: DLCI 301 - Router Barracuda is the “Hub” router and the other 2 routers are the “Spoke” routers.
- Do not change any configuration on the Frame-Relay switch.
- Configure the following IP addresses:
Router Barracuda:
S0/0: 192.168.123.1 /24
L0: 1.1.1.1 /24Router Salmon:
S0/0: 192.168.123.2 /24
L0: 2.2.2.2 /24Router Herring:
S0/0: 192.168.123.3 /24
L0: 3.3.3.3 /24 - Configure all serial interfaces for encapsulation Frame-Relay.
- Disable Frame-relay inverse arp on all serial interfaces.
- Configure the correct frame-relay map statements on all routers and make sure you can ping every IP address.
- Configure the OSPF network type to “point-to-multipoint” on all serial interfaces.
- Configure OSPF on all 3 routers, make sure you have full connectivity. All IP addresses including the loopbacks should be reachable.
- You are not allowed to use the “neighbor” command in the OSPF configuration.
It took me 1000s of hours reading books and doing labs, making mistakes over and over again until I mastered all the protocols for CCNP.
Would you like to be a master of networking too? In a short time without having to read 900 page books or google the answers to your questions and browsing through forums?
I collected all my knowledge and created a single ebook for you that has everything you need to know to become a master of CCNP.
You will learn all the secrets about OSPF network types, frame-relay settings and more.
Does this sound interesting to you? Take a look here and let me show you how to Master CCNP ROUTE!
IOS:
c3640-jk9s-mz.124-16.bin
Topology:
Video Solution:
Configuration Files
You need to register to download the GNS3 topology file. (Registration is free!)Once you are logged in you will find the configuration files right here.

The How to Master series helps you to understand complex topics like spanning-tree, VLANs, trunks, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP and more.
Written by René Molenaar - CCIE #41726


Final configs are empty
Realised that on Router Herring & Salmon OSPF works even without broadcast behind the frame-relay map command below?
Herring
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 301
Salmon
frame-relay map ip 192.168.123.1 201
If you enable "broadcast" on router Barracuda it will work. It will forward broadcast/multicast traffic between Herring and Salmon. Once it receives a broadcast on the PVC it will forward it onto the other PVC.
Final configs are empty
Hello!
Principal moment is exist in this lab. I want to draw your attention on the following fact.
If we have part mesh frame relay topology and we use point-to-multipoint ospf network, we shouldn’t configure additional FR mapping. This action is incorrect. When use PtMP in this lab, OSPF automatically creates several route. After run ospf-process Router R3 (Herring) have following routing table:
[code] 192.168.123.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O [b]192.168.123.2/32[/b] [110/128] via [b][i]192.168.123.1[/i][/b], 00 : 00:25, Serial0/0
O 192.168.123.1/32 [110/64] via 192.168.123.1, 00 : 00:25, Serial0/0
C 192.168.123.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 1.1.1.1 [110/65] via 192.168.123.1, 00 : 00:25, Serial0/0
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O [b]2.2.2.2 [/b][110/129] via [b][i]192.168.123.1[/i][/b], 00 : 00:25, Serial0/0
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 3.3.3.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
[/code]
I don’t configure FR mapping, but ping 2.2.2.2 from R3 is successful!
[code]HERRING#sh frame-relay map
Serial0/0 (up): ip 192.168.123.1 dlci 301(0x12D,0x48D0), dynamic, broadcast,, status defined, active
HERRING#ping 2.2.2.2 source 3.3.3.3
!!!!!
Success …
HERRING#ping 192.168.123.2
!!!!!
Success
[/code]
This same inaccuracy presents in the Odom’s book. if using part-mesh topology, only NBMA and broadcast OSPF network type require additional configuration Frame Relay mapping. This is due to the fact that in NBMA network includes DR router. And DR generates LSA Type 2. PtoMP don’t require additional FR-mapping.
Seems like you forgot to disable inverse-arp and/or did not clear inarp table
In my lab, Barracuda was not receiving the hello’s from the spokes and causing adjacency to drop and establish again, although spokes were sending out hello’s ever 30 sec.
So i had to add Broadcast wording to the map statements on the spokes to fix the issue.