Scenario
Since you are a excellent network engineer at the company you are working for, the network rarely has any problems and you have plenty of spare time. One of the days you were slacking off at the job and you implemented multicast on some of the routers to stream Star Trek videos across the network. Unfortunately some of your network colleagues found out and they are streaming some of their own videos using your configured rendezvous point (RP). Time to fix this before your the network is cluttered with useless video streams, after all you want your network career to be long and prosper…
Goal:
- All IP addresses have been preconfigured for you.
- Configure OSPF on all routers, achieve full connectivity.
- Configure sparse-mode multicast on all routers.
- Configure router Vulcan to be the rendezvous point (RP) in your network, use the loopback0 interface.
- Configure router Klingon to join the following 2 multicast groups:
224.1.1.1 (Star Trek videos)
224.2.2.2 (Company’s funniest home videos) - Configure router Vulcan so it only accepts the Star Trek video multicast group.
- Test this by pinging 224.1.1.1 and 224.2.2.2 from router Borg.
IOS:
c3640-jk9s-mz.124-16.bin
Topology:
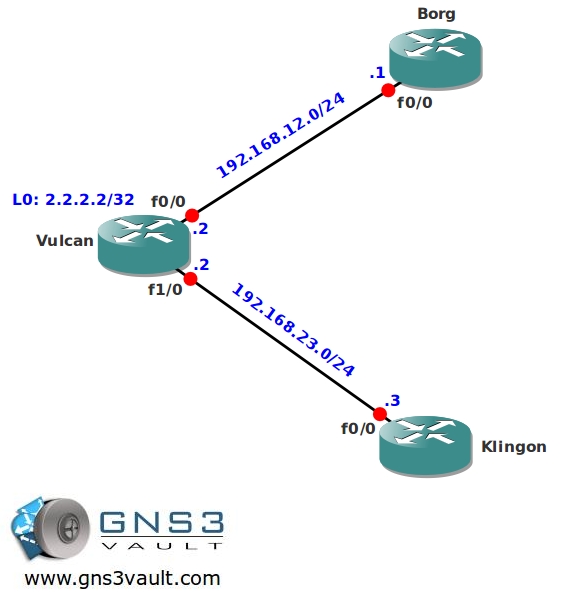
Video Solution:
Configuration Files
You need to register to download the GNS3 topology file. (Registration is free!)Once you are logged in you will find the configuration files right here.

The How to Master series helps you to understand complex topics like spanning-tree, VLANs, trunks, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP and more.
Written by René Molenaar - CCIE #41726


Thanks as always
Hi Rene
what is difference between accept-rp and accept-register?
accept-rp checks (*,G) joins to make sure they match the specified list (Standard)
accept-register is configured on RP only and checks the (S,G) information in the register to make sure they match the list (extended).
Is there a major difference between these two configs? Should you use one over the other? They both seem to perform the same function in this lab.
ip pim rp-address 2.2.2.2
ip pim accept-rp 2.2.2.2 1
access-list 1 permit 224.1.1.1
access-list 1 deny 224.2.2.2
________________________________________________________
ip pim rp-address 2.2.2.2 2
access-list 2 permit 224.1.1.1
access-list 2 deny 224.2.2.2